Third Trimester Screening Ultrasound and Blood Tests Explained

Sarah Johnson, MD
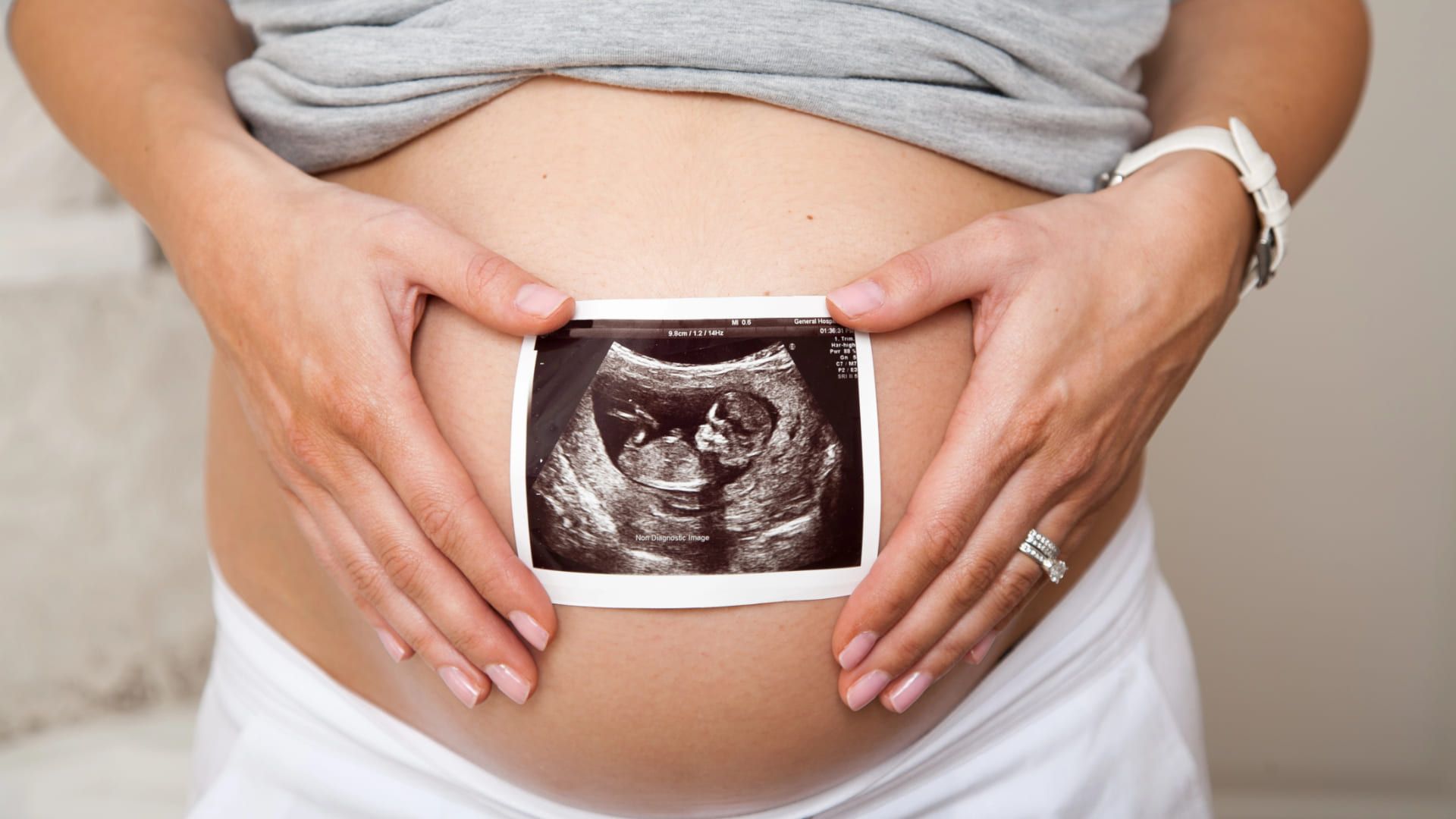
The third trimester is a time of mixed excitement and careful planning as you approach the end of your pregnancy. At May-Grant OB-GYN, which serves Lancaster, Pennsylvania, we are aware that screening tests at this point may raise a lot of questions. With the goal of arming you with knowledge for this pivotal phase of your pregnancy adventure, our blog attempts to navigate you through the confusing world of third-trimester screening tests.
- What is the Third trimester screening?
- What does the Third trimester screening include?
- When is the third trimester screening performed?
- What does the third trimester screening look for?
- Third trimester screening vs NIPT
- What do results of the third trimester screening mean?
- Next steps after the third trimester screening
What is the Third trimester screening?
There is intensive observation during the third trimester. An summary of several typical screening tests you may experience at this point in your pregnancy is provided here.

What does the Third trimester screening include?
- Glucose Screening Although glucose screening is usually done in the second trimester, your healthcare practitioner may decide to do another round of testing in the third trimester if you previously tested negative and have risk factors for gestational diabetes. What It Entails: You will drink a sugary beverage, and your blood will be extracted to measure your body's reaction to the sugar after a predetermined amount of time.
- Group B Strep (GBS) Test A common bacteria in the digestive system is GBS. While it poses no threat to adults, it can lead to severe illnesses in infants. What It Entails: Your rectum and vagina are sampled for testing. If the test is positive, the infant may be protected throughout labor by taking antibiotics.
- Biophysical Profile (BPP) An ultrasound and a non-stress test are combined in a BPP to assess your baby's general health. What It Entails: The non-stress test evaluates your baby's heart rate, while the ultrasound examines your baby's breathing, muscle tone, and movement in addition to the amount of amniotic fluid.
- Non-Stress Test This test tracks the heartbeat and response to movement of your baby. What It Entails: You have two monitors placed on your abdomen; one monitors the heartbeat of your unborn child, and the other measures the contractions.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound in the third trimester may be conducted, but it is not usually routine, to monitor your baby's growth, the placenta's position, or to address any concerns. What It Entails: An apparatus is placed over your abdomen that projects images of your unborn child onto sound waves.
When is the third trimester screening performed?
A scan for fetal growth and well-being is often carried out at approximately 36 weeks of pregnancy. Between 36 and 40 weeks, a second growth scan and color Doppler study are performed.
If you want a clearer week-by-week picture of what’s happening in your body at this stage, explore our overview of the third trimester by week to better understand how your symptoms and screening needs evolve.
What does the third trimester screening look for?
The main goal of screening tests throughout the third trimester is to protect the health and safety of both you and your unborn child. They aid in the detection of possible health problems that might call for further attention or care. This observation time gives you crucial information about the development of your pregnancy and gets you ready for labor and delivery.
Check Your Health Status: The tests evaluate your overall health, looking for diseases that could affect your pregnancy, such as preeclampsia or gestational diabetes.
Baby's Development: They keep an eye on the growth, mobility, and general health of your baby, monitoring their entire development and well-being.
Delivery Preparation: The tests assist in making well-informed decisions on your delivery process, including the mode of delivery and any postpartum special care your baby may require.
As you prepare for labor, supportive self-care practices can make this stage feel more manageable. Techniques like those described in our guide to breathing exercises for pregnancy may help ease tension and improve overall comfort during the third trimester.
Third trimester screening vs NIPT
The NIPT is a blood test that assesses minute DNA fragments circulating in the blood of a pregnant mother to ascertain the likelihood that the fetus would be born defectively. The NIPT looks for chromosomal abnormalities such trisomy 13, Down syndrome, and trisomy 18. While testing can be done as early as the second trimester, it is usually done during the first trimester.
A preliminary chromosomal screening for certain illnesses will probably be part of the first-trimester bloodwork that your doctor does. In the case of patients whose offspring are at a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities, they might also provide more sophisticated screenings, such as NIPT. These include mothers who are 35 years of age or older, mothers who have had a child with a genetic abnormality in the past, or mothers who have a family history of specific illnesses. Ask about all of your available options.
If you’re curious about how these changes connect to what your body is going through right now, our guide on what happens to the mother’s body in the third trimester offers a clear, supportive explanation.
What do results of the third trimester screening mean?
Test result interpretation can be difficult. We at May-Grant OB-GYN make sure to go over the results with you and help you comprehend what they represent for you and your child. Recall that an atypical result doesn't always indicate a problem; in fact, it frequently prompts additional testing to gain a better understanding.
Next steps after the third trimester screening
Your doctor can suggest a specialist labor and delivery center that can better meet your unique needs, or they might suggest early medical measures that can enhance the quality of life for your newborn.
If you are worried about your pregnancy, try Soula. Soul is AI assistant for Female Wellbeing.